Purpose:
Helps to gather statistics of system (IO, CPU), Database, Table, Columns,
Indexes.
This package will be executed
with the privileges of current_user.
How to
setup DBMS_STATS (Stats Pack) package:
Run script
[ORACLE_HOME]\rdbms\admin\spcreate.sql to create the package.
You'll need
to know three pieces of information before running the spcreate.sql script.
They are:
• The password you would like to use
for the PERFSTAT schema that will be created
• The default table space you would
like to use for PERFSTAT
• The temporary table space you would
like to use for PERFSTAT
Note: Use
spdrop.sql to remove the user and installed views prior to attempting another
install of StatsPack. The StatsPack installation will create a file called
spcpkg.lis. You should review this file for any possible errors that might have
occurred.
There are
three ways to collect statistics using dbms_stats package.
·
Automatic optimizer statistics collection
·
Mixed
·
Manual
How to gather Statistics using dbms_stats:
exec dbms_stats.gather_database_stats;
exec dbms_stats.gather_schema_stats('SCOTT');
exec dbms_stats.gather_table_stats
('SCOTT', 'EMP');
exec dbms_stats.gather_index_stats
('SCOTT', 'EMP_PK');
exec
dbms_stats.gather_dictionary_stats;
Delete statistics using dbms_stats:
exec dbms_stats.delete_database_stats;
exec dbms_stats.delete_schema_stats ('SCOTT');
exec dbms_stats.delete_table_stats ('SCOTT','EMP');
exec dbms_stats.delete_column_stats ('SCOTT', 'EMP', 'EMPNO');
exec dbms_stats.delete_index_stats ('SCOTT', 'EMP_PK');
exec
dbms_stats.delete_dictionary_stats;
EXEC DBMS_STATS.delete_system_stats;
Data Dictionary Views:
·
DBA_TABLES
·
DBA_TAB_STATISTICS
·
DBA_TAB_PARTITIONS
·
DBA_TAB_SUB_PARTITIONS
·
DBA_TAB_COLUMNS
·
DBA_TAB_COL_STATISTICS
·
DBA_PART_COL_STATISTICS
·
DBA_SUBPART_COL_STATISTICS
·
DBA_INDEXES
·
DBA_IND_STATISTICS
·
DBA_IND_PARTITIONS
·
DBA_IND_SUBPARTIONS
·
DBA_TAB_HISTOGRAMS
·
DBA_PART_HISTOGRAMS
·
DBA_SUBPART_HISTOGRAMS
More about histograms -> http://www.dba-oracle.com/t_histograms.htm
Q1:
SQL query to find the last time table is analyzed?
A1:
select last_analyzed
from dba_tables
where owner = 'OMSOWN'
and table_name = 'OEORDER_HEADER'
Q2:
SQL to find whether the table is partitioned or not? If partitioned, then
display the names of the partitions.
A2: select partitioned
from dba_tables
where owner = 'OMSOWN'
and table_name = 'OEORDER_HEADER'
select * from
dba_tab_partitions
where table_owner = 'OMSOWN'
and table_name = 'OEORDER_HEADER'
System Stats:
Gather_system_stats
gathers statistics related to the performance of I/O and CPU.
-- Manually start
and stop to sample a representative time (several hours) of system activity.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.gather_system_stats('start');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.gather_system_stats('stop');
-- Sample from now
until a specific number of minutes.
DBMS_STATS.gather_system_stats('interval', interval => 180);
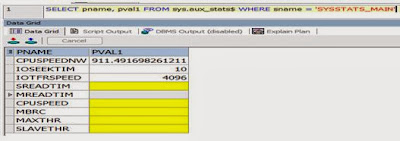
Q3:
Write a query to display current system statistics
A3: SELECT pname, pval1 FROM sys.aux_stats$
WHERE sname = 'SYSSTATS_MAIN';
EXEC DBMS_STATS.gather_fixed_objects_stats; -- To gather
statistics on the X$ tables
EXEC DBMS_STATS.delete_fixed_objects_stats; -- To
delete statistics
Locking Stats:
To prevent statistics being overwritten, you can lock the stats at schema, table or partition level.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.lock_schema_stats('SCOTT');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.lock_table_stats('SCOTT', 'EMP');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.lock_partition_stats('SCOTT', 'EMP', 'EMP_PART1');
If you need to replace the stats, they must be
unlocked.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.unlock_schema_stats('SCOTT');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.unlock_table_stats('SCOTT', 'EMP');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.unlock_partition_stats('SCOTT', 'EMP', 'EMP_PART1');
Transferring Stats:
It is possible to transfer statistics between servers allowing consistent execution plans between servers with varying amounts of data.
First the statistics must be collected into a statistics table. In the following examples the statistics for the APPSCHEMA user are collected into a new table, STATS_TABLE, which is owned by DBASCHEMA.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.create_stat_table('DBASCHEMA','STATS_TABLE');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.export_schema_stats('APPSCHEMA','STATS_TABLE',NULL,'DBASCHEMA');
This table can then be transfered to another server using your preferred method (Export/Import, SQL*Plus COPY etc.) and the stats imported into the data dictionary as follows.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.import_schema_stats('APPSCHEMA','STATS_TABLE',NULL,'DBASCHEMA');
EXEC DBMS_STATS.drop_stat_table('DBASCHEMA','STATS_TABLE');
Setting Stats Manually:
The DBMS_STATS package provides several
procedures for manually setting statistics.
SET_SYSTEM_STATS
SET_TABLE_STATS
SET_COLUMN_STATS
SET_INDEX_STATS
The current stats can be returned using the following procedures.
GET_SYSTEM_STATS
GET_TABLE_STATS
GET_COLUMN_STATS
GET_INDEX_STATS
Be careful when setting stats
manually. Possibly the safest approach is to get the current values, amend them as required, then set them. An example of setting column statistics is shown below.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON
DECLARE
l_distcnt NUMBER;
l_density NUMBER;
l_nullcnt NUMBER;
l_srec DBMS_STATS.StatRec;
l_avgclen NUMBER;
BEGIN
-- Get
current values.
DBMS_STATS.get_column_stats (
ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
colname => 'EMPNO',
distcnt => l_distcnt,
density => l_density,
nullcnt => l_nullcnt,
srec => l_srec,
avgclen => l_avgclen);
-- Amend
values.
l_srec.minval := UTL_RAW.cast_from_number(7369);
l_srec.maxval := UTL_RAW.cast_from_number(7934);
-- Set
new values.
DBMS_STATS.set_column_stats (
ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
colname => 'EMPNO',
distcnt => l_distcnt,
density => l_density,
nullcnt => l_nullcnt,
srec => l_srec,
avgclen => l_avgclen);
END;
/
Optimizer statistics include the following:
·
Table statistics
o Number
of rows
o Number
of blocks
o Average
row length
·
Column statistics
o Number
of distinct values (NDV) in column
o Number
of nulls in column
o Data
distribution (histogram)
o Extended
statistics
·
Index statistics
o Number
of leaf blocks
o Levels
o Clustering
factor
·
System statistics
o I/O
performance and utilization
o CPU
performance and utilization
Automatic Optimizer Statistics Collection:
If this
option enabled, the database automatically collects optimizer statistics for
tables with absent or stale statistics.
Automatic optimizer statistics collection
calls the DBMS_STATS.GATHER_DATABASE_STATS_JOB_PROC procedure. This internal procedure operates
similarly to the DBMS_STATS.GATHER_DATABASE_STATS procedure using the GATHER AUTO option. The main difference is that GATHER_DATABASE_STATS_JOB_PROC prioritizes database objects that require statistics, so
that objects that most need updated statistics are processed first, before the
maintenance window closes.
BEGIN
DBMS_AUTO_TASK_ADMIN.ENABLE(
client_name => 'auto optimizer stats collection',
operation => NULL,
window_name => NULL);
END;
/
BEGIN
DBMS_AUTO_TASK_ADMIN.DISABLE(
client_name => 'auto optimizer stats collection',
operation => NULL,
window_name => NULL);
END;
/
When to Use Manual Statistics:
1.
When large bulk loads performed on a table
(generally 10% or more of total records changed)
2.
When tables deleted or truncated and rebuild
during the course of the day
How to determining the Stale Statistics:
When the STATISTICS_LEVEL parameter
is set to TYPICAL or ALL then monitoring is enabled by default to determine
whether a given database objects needs new database statistics or not.
Oracle
provides a table monitoring facility which tracks the approximate number of
rows inserted, updated & deleted.
Query the
view USER_TAB_MODIFICATIONS
Note: Analyze statement, dbms_utility.analyze_schema,
dbms_utility.analyze_database are maintaining for backward compatibility.

No comments:
Post a Comment